Products and features
Products, Environmental measures
-
What are RoHS, WEEE, and ELV?
-
The RoHS Directive was amended in 2011 to RoHS2, which restricts or prohibits the use of additional cadmium, lead, mercury, hexavalent chromium, PBB (polybrominated biphenyls), PBDE (polybrominated diphenyl ethers), and four phthalate esters (DEHP, BBP, DBP, DIBP).
Each of these 10 substances in total has a maximum allowable concentration, and products containing amounts exceeding the maximum allowable concentration cannot be manufactured or sold in the EU.
These “directives” are EU directives, and since any product distributed within the EU is subject to regulation, many Japanese companies that manufacture export products are also affected. Furthermore, even if they do not export their products directly into the EU, they are required to provide retroactive warranties if products incorporating their products are exported.”The WEEE and RoHS Directives were simultaneously published in 2003 as EU Directives on the recycling of electrical and electronic equipment and hazardous substances.
The WEEE Directive (Waste electrical and electronic equipment) encourages and requires recycling with the aim of reducing the final disposal of waste electrical and electronic equipment.
The RoHS Directive (Restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in the electrical and electronic equipment) regulates the substances contained in electrical and electronic equipment with the aim of preventing products containing more than a certain percentage of hazardous substances from being placed on the market.The ELV Directive (End-of Life Vehicle) is is an EU directive issued in 2000 that has two requirements for motor vehicles: recycling requirements and content restrictions on certain hazardous substances.
The ELV Directive prohibits the inclusion of lead, mercury, cadmium, and hexavalent chromium in materials and parts of automobiles sold in the market in concentrations higher than the permissible levels, with the exception of certain items. -
What are the meanings of X and Q used in the ink names such as IPX, INQ, FMX, etc.?
-
X and Q are used to designate isophorone-free inks.
IR Transmittable, Luminescent function, others
-
What is diffusivity?
-
We refer to the diffusion of light (Haze: cloudiness). By diffusing light, a frosted glass-like effect can be achieved.
-
What is Phosphorescent ink?
-
Phosphorescent ink contains pigments with luminescent properties that absorb and accumulate light rays from the sun, electric lights, etc., and gradually emit them, so the absorption-accumulation-emission process can be repeated many times. It can also be applied to safety and energy saving measures.
Related Links
Introduction of Luminova Phosphorescent Ink
Product Information: Phosphorescence Ink
Luminova Phosphorescent ink -
What is dead front (concealed) printing applying the IR transparency function?
-
As mentioned above, IR transmittable inks allow control of transmittable colors, and variation in hue can be achieved by overprint with metallic inks. Therefore, various decorations are possible with “dead front (concealed) printing,” printing that cannot be seen unless illuminated by light.
Note1) Transmittance varies slightly depending on the transmitted color.
Note2) Infrared transmittance decreases by 10-20% when over printed with metallic inks. Related Links Introduction of IR Transmittable Ink and Dead front PrintingRelated Links
Introduction of IR transmittable ink (IR Transmitting Ink) and concealed printing -
How do you use IR transmittable ink (IR Transmitting Ink) ?
-
After printing IR transmittable ink (IR Transmitting Ink) onto transparent PC or PET substrate sheet, the ink has the special function of blocking the shorter wave-length visible rays and ultra violet rays and allows the longer wave-length infrared rays to penetrate. One example of an application that this ink is used for is the signal receiving filter of remote control devices.
Jet Black, High Opacity, Non-conductive, Others
-
Is there any information related to high transparency inks?
-
The MIX-HF ink series offers “High transparency” and “excellent leveling property” more than ever before. The haze value in MIX-HF000 medium (*) is as low as 0.6. In addition to MIX-HF, there are other inks with high transparency such as TOC-HF. Please select the ink that best suits your application.
(*) Haze value: Haze value is the ratio of diffuse light transmission to total light transmission when irradiated with visible light. The smaller the haze value, the better the transparency.
Haze value(%)=Td/Tt x 100 (Td:Diffusive transmittance, Tt: Total transmittance)Related link:
Introduction of MIX-HF (2)
Introduction of TOC-HF transmittance ink (1) -
What is non-conductive black ink?
-
Non-Conductive Black Ink is an ink that has a high electrical resistance of the printed ink layer, and has both a function that is difficult for electricity to pass through and a high opaque black color. The high electrical resistance (low conductivity) prevents malfunctions and failures of electronic components, etc., caused by electric current flowing through the printed ink layer. Furthermore, its high opacity makes it suitable for printing on flat panels and smartphone displays that require light-shielding properties.
Related Link
Introduction of Functional Black Ink -
What is high opacity black and white?
-
This function provides a beautiful black or white color with high opacity even in environments where backlights are used, such as outer frames of flat panels and touch panels.
Related link
Introduction of GLS-HF (3) -
What is jet-black ink?
-
Jet-Black ink is an ink that produces a glossy black finish called “piano black” or “jet black. It achieves a luxurious lacquer-like gloss and unique brilliance, and contributes to the high added value of the products .
Related link
Introduction of functional Black ink
Mirror ink in general
-
Is Mirror Ink patented?
-
Yes it is patented. (Japanese Patent Registered Number 3151606)
The patent covers the manufacturing method of Mirror Ink, making prints with Mirror ink and making prints with similar ink.
-
What is the meaning of mirror effect technology?
-
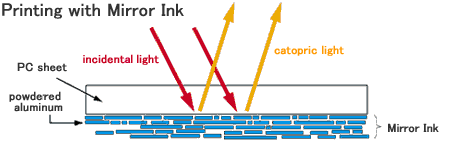
Mirror ink is applied onto PC or PET material sheet by screen printing, which results in a mirror effect similar to metal plating.
-
Is it possible to add color to mirror ink?
-
Mirror inks are available in a variety of colors. Vivid colors and high mirror effect can be achieved by combining with transparent ink. Please refer to the following to select the ink that best suits your application.
Related link
Introduction of MIX-HF (1)
Introduction of TOC-HF transmittance ink (2)
Caution for using Mirror ink
-
What is the recommended applicable substrate?
-
The applicable substrates for MIR-Ink are PC and treated PET (MIR ink does not adhere to untreated PET, eveb if it is a PET substrate).
However, adhesion varies depending on the grade of PC and treated PET. In addition, for hard coat materials and acrylic materials, it is necessary to individually select inks and check adhesion.
-
What is the recommended overprint ink?
-
Please use MIX-HF ink for MIR-ink for over printing. If other inks are used, the mirror effect will deteriorate.
However, for substrates with strong solvent resistance (treated PET), inks other than MIB and MIX-HF inks can also be used as a overprint ink.
-
What information do you have on how to handle inks that affect mirror effect?
-
Be sure to stir mirror inks before printing. Some of the components may be separated, but stirring will make them uniform. Insufficient stirring may cause streaking or unevenness.
Do not return ink to the container of unused ink after printing. Ink remaining on the stencil will cause aluminum to agglomerate with each other, and printing again may cause a decrease in mirror effect quality, as well as the occurrence of streaking and unevenness. The above problems may occur if used ink is used, so please avoid using used ink.
Regarding the supply of ink, it is more efficient to use ink by pouring ink little by little onto the stencil than to put the amount of ink required for printing on the stencil at once.
-
What is the information on printing conditions that affect mirror effect?
-
Printing pressure and doctor pressure are important in printing conditions. Mirror ink provides mirror effect and opacity by orienting aluminum pigments. Therefore, in order to orient the aluminum pigments, the printing pressure and doctor pressure should be set higher than for general solid inks.
Thicker film thickness (3μ or more) may cause delamination in the aluminum layers. In addition, mirror surface will be reduced, causing unevenness. As for opacity, thicker film thickness improves opacity, but if the aluminum pigments are well oriented, opacity can be obtained even with a thin film thickness.
Stable quality (mirror effect and opacity) of printed materials can be obtained by printing recommended conditions described in 1-2 Screen stencil, 1-3 Squeege, 2-2 Drying conditions, and 2-3 Printing conditions.
-
What is the information on drying conditions that affect mirror effect?
-
For non-solvent-resistant substrate (PC), mirror effect properties are greatly affected by drying conditions. This is especially true for PC molded products. The optimal drying conditions vary depending on the grade of PC resin used, molding conditions, etc.
Mirror effect can be obtained by initial drying at low temperature and subsequent drying at high temperature. (Initial drying at low temperatures suppresses the effects of solvent attack and improves the mirror effect because the aluminum pigments are well oriented.)
-
What is the information on substrate (base material) that affect mirror effect?
-
Drying conditions vary depending on the type of substrate.
In case of MI-51000 Mirror ink series, drying condition is 80℃, 30 min. for both PC and treated PET, but for PC, initial drying at low temperature followed by high temperature drying (80°C for 30 minutes) will give a more mirror effect.
-
What is the recommended preliminary test?
-
Be sure to conduct a preliminary test under similar printing conditions before printing on the main line. The preliminary test procedure is as follows.
1. Print mirror ink on the substrate to be printed on the main line (substitutes are not acceptable) and dry under the conditions described in the catalog.
2. Conduct test on mirror effect, opacity, and adhesion, etc.
3. If it fails, adjust the printing and drying conditions to obtain satisfactory results.Repeat the above tests until appropriate conditions are found.
-
What is the recommended viscosity adjustment?
-
Mirror inks do not require dilution at the time of use. However, it should be stirred well before use.
-
What is the recommended screen stencil?
-
The finish of mirror ink prints varies depending on the type of screen stencil used. The items of a screen stencil suitable for printing mirror ink are stencil mesh, opening, line diameter, and emulsion thickness. Recommended conditions for printing stencil are a stencil mesh of T-300, a wide opening, a narrow line length, and a thin emulsion thickness (6 to 8 µm).
-
What is recommended environmental conditions?
-
When printing MIR-Mirror Ink series, please adjust the temperature and humidity to keep them constant as printing working conditions. Recommended conditions are temperature: 20-25℃, humidity: 50±5%Rh. If the printing working conditions become too hot or too humid, mirror ink absorbs moisture, resulting in a decrease in mirror effect and opacity, and stable printing is not possible.
-
What are some of the differences between mirror ink and general solvent ink that should be noted?
-
In order to provide mirror effect, the composition of Mirror Ink differs greatly from that of general solvent type inks.
The composition of mirror ink is mainly resin, aluminum pigment, and solvent, but the resin to solvent ratio is different compared to general solvent type inks. Therefore, there are differences in performance, such as printability, between mirror ink and general solvent type ink.
Troubleshooting Mirror ink
-
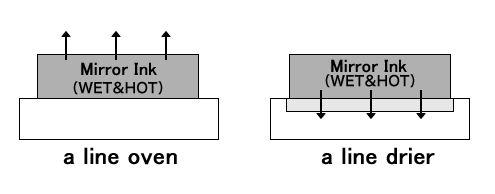
When drying the print in a line oven it sometimes appears hazy. Why does this occur?
-
Upon further investigation with the customer, the printing conditions that caused this hazy appearance were discovered to be as follows. Mirror Ink was printed with a cylinder press and dried in a line dryer at a high temperature, thus the resultant hazy effect. The reason being: the initial drying at a high temperature. The recommended drying condition is 30 minutes at 80°C, but in this case the line dryer was used for 2 minutes at 100°C. When the substrate was dried at this high temperature with a great deal of solvent on it, the substrate was affected adversely and turned white.
-
How can we dry in a line dryer without getting haze?
-
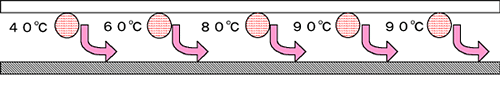
You may avoid the hazy effect with following countermeasures:
1. Lower the temperature of the line dryer. (lower than 80°C)
2. If the line dryer has several drying sections, set the temperature at the entrance section as low as 40-60°C and evaporate the solvent as much as possible (preferably 80-90%).
3. Then the printed matter can be dried at 80-100°C and evaporate the solvent completely. This should result in a good mirror effect.
-
Is over-printing required?
-
Yes. Over-printing is necessary not only to improve scratch resistance but also to improve resistance to other elements. As Mirror Ink is affected by moisture, the aluminum layer might change the color if not over-printed.
-
How can we increase covering power?
-
Use squeegee with 70 degree hardness and rather high printing pressure. When printing with Mirror Ink, the covering power may not be as good as what is shown in print samples. An effective measure to increase covering power is to use a harder squeegee. As the Mirror Ink has less resin in it, ink transfer to the substrate is rather lighter than with ordinary screen inks.
Therefore changing printing conditions is sometimes effective.
* Recommended printing conditions are as follows
Squeegee hardness should be 70 degrees. / Printing pressure should be slightly higher. / Doctor pressure should be slightly higher as well.